After centuries of political and territorial divisions, Italy was almost entirely unified in 1861, following wars of independence and the Expedition of the Thousand, establishing the Kingdom of Italy. From the late 19th to the early 20th century, Italy rapidly industrialised—mainly in the north—and acquired a colonial empire, while the south remained largely impoverished, fueling a large immigrant diaspora to the Americas. From 1915 to 1918, Italy took part in World War I with the Entente against the Central Powers. In 1922, the Italian fascist dictatorship was established. During World War II, Italy was first part of the Axis until its surrender to the Allied powers (1940–1943), then a co-belligerent of the Allies during the Italian resistance and the liberation of Italy (1943–1945). Following the war, the monarchy was replaced by a republic and the country enjoyed a strong recovery.
A developed country with an advanced economy, Italy has the ninth-largest nominal GDP in the world, the second-largest manufacturing sector in Europe, and plays a significant role in regional and—to a lesser extent—global economic, military, cultural, and political affairs. Italy is a founding and leading member of the European Union, and is part of numerous other international organizations and forums. As a cultural superpower, Italy has long been a renowned global centre of art, music, literature, cuisine, fashion, science and technology, and the source of multiple inventions and discoveries. It has the highest number of World Heritage Sites (60) and is the fourth-most visited country in the world.
Hypotheses for the etymology of Italia are numerous.[13] One theory suggests it originated from an Ancient Greek term for the land of the Italói, a tribe that resided in the region now known as Calabria. Originally thought to be named Vituli, some scholars suggest their totemic animal to be the calf (Latin: vitulus; Umbrian: vitlo; Oscan: Víteliú).[14] Several ancient authors said it was named after a local ruler Italus
The ancient Greek term for Italy initially referred only to the south of the Bruttium peninsula and parts of Catanzaro and Vibo Valentia. The larger concept of Oenotria and "Italy" became synonymous, and the name applied to most of Lucania as well. Before the Roman Republic's expansion, the name was used by Greeks for the land between the strait of Messina and the line connecting the gulfs of Salerno and Taranto, corresponding to Calabria. The Greeks came to apply "Italia" to a larger region.[16] In addition to the "Greek Italy" in the south, historians have suggested the existence of an "Etruscan Italy", which consisted of areas of central Italy.[17]
The borders of Roman Italy, Italia, are better established. Cato's Origines describes Italy as the entire peninsula south of the Alps.[18] In 264 BC, Roman Italy extended from the Arno and Rubicon rivers of the centre-north to the entire south. The northern area, Cisalpine Gaul, considered geographically part of Italy, was occupied by Rome in the 220s BC,[19] but remained politically separated. It was legally merged into the administrative unit of Italy in 42 BC.[20] Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, and Malta were added to Italy by Diocletian in 292 AD,[21] which made late-ancient Italy coterminous with the modern Italian geographical region.
Ancient Rome
Italy's history goes back to numerous Italic peoples—notably including the ancient Romans, who conquered the Mediterranean world during the Roman Republic and ruled it for centuries during the Roman Empire.[35]
Ancient Rome, a settlement on the River Tiber in central Italy, founded in 753 BC, was ruled for 244 years by a monarchical system.[36] In 509 BC, the Romans, favouring a government of the Senate and the People (SPQR), expelled the monarchy and established an oligarchic republic.[37]
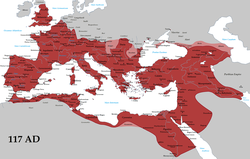
The Italian Peninsula, named Italia, was consolidated into a unified entity during Roman expansion, the conquest of new territories often at the expense of the other Italic tribes, Etruscans, Celts, and Greeks. A permanent association, with most of the local tribes and cities, was formed, and Rome began the conquest of Western Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. In the wake of Julius Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Rome grew into a massive empire stretching from Britain to the borders of Persia, engulfing the whole Mediterranean basin, in which Greek, Roman, and other cultures merged into a powerful civilisation. The long reign of the first emperor, Augustus, began an age of peace and prosperity. Roman Italy remained the metropole of the empire, homeland of the Romans and territory of the capital.[38]
The Roman Empire was among the largest in history, wielding great economical, cultural, political, and military power.[39] At its greatest extent, it had an area of 5 million square kilometres (1.9 million square miles).[40] The Roman legacy has deeply influenced Western civilisation shaping the modern world. The widespread use of Romance languages derived from Latin, numerical system, modern Western alphabet and calendar, and the emergence of Christianity as a world religion, are among the many legacies of Roman dominance.